Federico Sesti
Professor
Bio
Federico Sesti is a Professor at the Department of Neuroscience and Cell Biology. He received his PhD in Physics from the Universita' di Genova in Italy and completed his postdoctoral training at Forschungszentrum and Yale University. He has provided the following statement on the work done in his lab:
K+ channels are integral membrane proteins whose primary function in the nervous system, is to modulate the wide variety of firing patterns that are required for processing information and generating motor outputs. In addition, K+ channels can also control cellular functions in ways that do not directly depend on their conducting properties. Channels engage receptors and other signaling molecules to perform non-ionic roles, especially integrins, which play multi-faceted roles in cell signaling.
For more than a decade the laboratory has been studying non-ionic functions of K+ channels. We focus on a multifunctional complex--formed by the voltage-gated K+ channel KCNB1 (Kv2.1) and integrin 5/ 5--that we recently named integrin-KCNB1 complex or IKC. These complexes are sensors of membrane excitability that transduce the electrical activity at the membrane (via the channel) into intracellular signals (via integrins) that modulate fundamental properties of the cell, such as migration and survival.
A distinctive trait of integrin-KCNB1 complexes is that they act as beneficial molecules early in life but become deleterious late in life through largely conserved mechanisms. Alzheimer's disease and Traumatic Brain Injury provide examples of the pleiotropic nature of integrin-KCNB1 complexes. As the brain undergoes neurodegeneration or trauma, these complexes turn toxic and cause neuronal inflammation and loss via the signaling machinery of integrins.
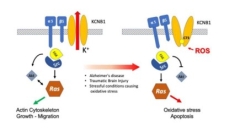
Our studies show that stimulation of integrin-KCNB1 complexes leads to the engagement of Focal Adhesion kinase (FAK), Src family tyrosine kinases, Ras GTPases, and Protein kinase B (Akt) resulting in cytoskeletal remodeling, proliferation, and growth. In the presence of significant oxidative stress (the imbalance between reactive oxygen species, ROS, and antioxidants), like in the Alzheimer's brain or following a brain trauma, the ROS causes irreversible structural modifications in KCNB1 channels (cross-linking).
These modifications are interpreted by the integrins as detachment from the extracellular matrix, a requirement for survival. Consequently, the signaling pathway diverges at some point downstream Ras inducing the activation of via MAPK family c-Jun N-terminal kinases, which promote oxidative stress and eventually cellular death. Current projects focus on elucidating the role of integrin-KCNB1 signaling in Alzheimer's disease and Traumatic Brain Injury. We are also assessing the potential therapeutic of second-generation Bcr-Abl and Src tyrosine kinase inhibitors and BACE1 inhibitors for treating those pathologies.
Current Funding
National Institutes of Aging Health, National Institutes of Health
Publications
Selected Publications
- Yu W., M. Shin, F. Sesti (2019). "Complexes formed with integrin- 5 and KCNB1 potassium channel wild type or epilepsy-susceptibility variants modulate cellular plasticity via Ras and Akt signaling". FASEB J. 33(12): 14680-9. doi: 10.1096/fj.201901792R.
- Yu W, M. Shin, F. Sesti (2018) "Oxidation of KCNB1 channels in the human brain and in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease", Cell Death Dis. (2018) 9(8):820, doi:10.1038/s41419-018-0886-1
- Yu W., R. Parakrama, S. Teng, M. Gowda, Y. Sharad, S. Thakker-Varia, J. Alder, F. Sesti (2016) “Oxidation of KCNB1 Potassium Channels Causes Neurotoxicity and Cognitive Impairment in a Mouse Model of Traumatic Brain Injury”. J. Neurosci. 36(43):11084 –11096.
- Duan Z. and F. Sesti (2015). “Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor OSG-1 Confers Functional Aging via Dysregulated Rho Signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans Neurons.” Genetics 199(2):487-96.
- Cotella D., B. Hernandez, X. Wu, R. Li, Z. Pan, J. Leveille, C.D. Link, S. Oddo, and F. Sesti (2012). Toxic role of K+ channel oxidation in mammalian brain. J. Neurosci., 32(12):4133-44.
- Sesti F., S. Liu and S. Cai (2010). "Oxidation of K+ channels by ROS: a general mechanism of aging and neurodegeneration?”. Trends in Cell Biology, 20(1):45-51.
- Cai S., Y. Wang, K.H. Park, X. Tong, Z. Pan, F. Sesti (2009). Auto-phosphorylation of a voltage-gated K + channel controls non-associative learning. EMBO J. 28(11):1601-10.
- Cai S. and F. Sesti (2009). Oxidation of a potassium channel causes progressive sensory function loss during aging. Nature Neurosci., 12(5):611-7.
- Cai S., L. Hernandez, Y. Wang, K.H. Park, F. Sesti (2005) “MPS-1 is a K+ channel -subunit and a serine/threonine kinase” Nature Neurosci. 8(11):1503-9.
