Cystic Fibrosis Center
Our Mission
The mission of the Cystic Fibrosis Center is to be a world leader in cystic fibrosis care, education and research by using an interdisciplinary approach in:
- practicing family centered, evidenced-based clinical care across the life span
- developing common goals in partnership with patients and families to enhance quality of life
- providing quality professional education
- promoting innovative research
The Cystic Fibrosis Center at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School-Bristol Myers Squibb Children's Hospital at Robert Wood Johnson University Hospital is one of only 3 Level III CF centers is the state of NJ that is accredited by the national CF Foundation. The Adult CF center at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School at Robert Wood Johnson University Hospital received accreditation by the National CF Foundation in 2007. The CF Center at RWJ cares for approximately 130 patients and their families.
What is Cystic Fibrosis?
Cystic Fibrosis (CF) is a chronic progressive life shortening disease, with multiple organ system involvement and requires a coordinated multidisciplinary approach to provide comprehensive care in order to improve outcomes. Due to the chronicity of the disease, there is a tremendous psychosocial and financial burden to the individual, family and society. Numerous studies show that patients who receive care in an accredited CF center have better outcomes. Our staff is abreast of new recommendations set forth by the CF Foundation and we update our management protocols to comply with these.
Our goal as a center is to continue to provide excellent state of the art comprehensive care to all patients so that no patient with cystic fibrosis will have to leave the state to receive appropriate care. In order to achieve this goal, it is necessary to have an interdisciplinary team, which includes:
- Physicians
- Nurse Practitioners, Clinic Nurse Coordinators
- Registered Nurses
- Respiratory Therapists
- Nutritionists
- Social Worker
Our Services
- Comprehensive ambulatory and inpatient care
- Evaluation
- Testing
- Clinical Management
- Nutritional education and management
- Counseling, case management and advocacy
- Life long follow up care
- Comprehensive education programs for families, community providers and other health care professionals on the care of CF patients
- Services are provided both to the CF patient and his/her family as needed.
Outpatient Services
Outpatient Services Provided in Cooperation with BMSCH and RWJUH include:
- Sweat Testing
- Pulmonary Function Testing
- Diagnostic Imaging, including MRI, ultrasound and CT
- Bone Density Scans
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Testing
- Sputum Culture
Inpatient Care for pediatric and adolescent patients at BMSCH at RWJUH, for adult patients at RWJUH. Faculty and staff in the CF program follow patients both outpatient and inpatient. Center physicians provide 24 hour, 7 day per week care.
Message from the Chief
Dear Patients and Families,
This website contains information which will begin your orientation to Cystic Fibrosis. It will also introduce you to our Cystic Fibrosis Center at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School/UMDNJ and keep you up to date on what is going on at our center. Last, it will orient you to Bristol Myers Squibb Children’s Hospital and Robert Wood Johnson University Hospital. We realize the tremendous effect that a new diagnosis has on your family and we believe that a website such as this will serve as a starting point to help you and your family address the challenges posed by CF. We also believe this website can be useful over the life span as CF presents challenges and opportunities at different stages.
Over the years we have had the privilege of helping many families and patients successfully cope with the challenges presented by CF. Our goal in developing this website is to provide background information and resources to help you along that journey. In early childhood, much of the care for your child will be provided by yourselves and your family in your home. Later in life, the care is handed over to your adolescent or young adult and our patients and their support systems will be responsible for their own care. We would like to serve as advisors, teachers and an extended support system for you and your family along the way.
This website will also be updated as new information and guidance becomes available. Often times, in the anxiety over a visit to the hospital or the clinic, much of what is said is not clearly remembered once you are home. We hope that this site, along written care plans you receive in clinic will answer your questions and give you helpful guidance.
This website and the education received from all members of our team and other professionals in the field will serve as a firm foundation for building a lasting and successful partnership in our mutual goal of helping your child or family member successfully cope with Cystic Fibrosis. Our ultimate mutual goal is to insure that your family member has a full, productive life.
As always, feel free to call our office with any questions. Our multidisciplinary team is here to provide education and support.
- Pediatric Program can be reached at 732-235-7899
- Adult Program can be reached at 732-235-7840.
Sincerely,
Thomas F Scanlin, MD
Director, Cystic Fibrosis Center
Sabiha Hussain, MD
Adult Program Director
Pediatric Care Team
- Center Director: Thomas Scanlin, MD
- Associate Director: Maya Ramagopal, MD
- Assistant Professor: Lakshmi Uppaluri, MD
- CF Center Coordinator / Social Worker: Erin McElroy Barker, LCSW
- Pediatric Nurse Practitioners: Chinwe Izegbu, MSN, RN, APN-C Dawn Tortajada, MSN, RN, APN-C Nurse: Lillian Saturria, RN
- Dietician: Daria Mintz, RD
- Respiratory Therapist: Eddy Paredes, RRT
- Department Secretary: Vivian De Los Santos
Part Time Team Members:
- Psychologist: Amanda Morales Clarke, Psy D
- Pharmacist: Eileen Harrington
- Physical Therapist: MaryJane Myslinski, PT, EdD
Adult Care Team
- Program Director: Sabiha Hussain, MD
- Assistant Director: Sugeet Jagpal, MD
- CF Center Coordinator/Social Worker: Erin McElroy Barker, LCSW
- Dietician: Rachna Singh, RD, CDE
- Nurse Practitioner: Chinwe Izegbu, MSN, RN, APN-C
- Pulmonary Nurse: Cathy Trillo, RN
- Respiratory Therapist: Paula Marulanda, RT
Part Time Team Members:
- Psychologist - Amanda Morales-Clarke PsyD
- Pharmacist - Eileen Harrington
- Physical Therapist - MaryJane Myslinski, PT, EdD
News
Calling All Adult Patients
The Cystic Fibrosis Foundation is launching the Adult Guide to Cystic Fibrosis, a new online educational resource written just for adults with CF. The Adult Guide covers a range of topics including the basics of lung care, male infertility, pregnancy, menopause, parenting as an adult with CF, and traveling with CF.
To help the CF Foundation improve the information in the guide, they welcome your feedback by completing a short survey.
Events
Great Strides - Cystic Fibrosis Foundation
Great Strides is a national walk held annually to raise funds for the CF Foundation as well as awareness about CF. We encourage and welcome you to join this effort by building your own team, joining a team or joining our team. There are local walks all over the country for those who want to go local. This year, the CF Team at RWJMS will be joining the newest walk site in NJ:
Woodlot Park
1224 New Road, Monmouth Junction
Registration Starts at 10 AM, Walk starts at 11 AM.
Family Advisory Council
If you are a family member of a pediatric or adult patient and would like to have a voice in the efforts of this center, please call us and volunteer to join this group. Meetings will be held quarterly and you can participate by conference call. Call Erin at 732-235-6409 if interested or email at mcelroer@rwjms.rutgers.edu.
Directions
Pediatric/Adolescent CF Center
Child Health Institute of New Jersey
89 French Street, Suite 2300
New Brunswick, NJ 08901
Adult CF Program
Clinical Academic Building (CAB)
125 Paterson Street, Suite 5200B
New Brunswick, NJ 08901
Overview
According to the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation, Cystic fibrosis is an inherited chronic disease that affects the lungs and digestive system of about 30,000 children and adults in the United States (70,000 worldwide). A defective gene and its protein product cause the body to produce unusually thick, sticky mucus that:
- clogs the lungs and leads to life-threatening lung infections; and
- obstructs the pancreas and stops natural enzymes from helping the body break down and absorb food.
In the 1950s, few children with cystic fibrosis lived to attend elementary school. Today, advances in research and medical treatments have further enhanced and extended life for children and adults with CF. Many people with the disease can now expect to live into their 30s, 40s and beyond.
Symptoms of Cystic Fibrosis
People with CF can have a variety of symptoms, including:
- very salty-tasting skin;
- persistent coughing, at times with phlegm;
- frequent lung infections;
- wheezing or shortness of breath;
- poor growth/weight gain in spite of a good appetite; and
- frequent greasy, bulky stools or difficulty in bowel movements.
Statistics
- About 1,000 new cases of cystic fibrosis are diagnosed each year.
- More than 70% of patients are diagnosed by age two.
- More than 45% of the CF patient population is age 18 or older.
- The predicted median age of survival for a person with CF is in the late 30s.
Most Common Problems
The two most common problems in CF, partly caused by abnormal mucus, involve the lungs (respiratory system) and the digestive system. The body makes mucus as a way to keep itself lubricated and clean (rather like motor oil in a car engine). In healthy people, the lungs and the digestive tract both make mucus. In people with CF, the body makes mucus, but the mucus is different; it is much thicker and stickier. Abnormal mucus causes several problems. The thick and sticky mucus in the lungs of people with CF is hard to cough up. When mucus stays in the lungs, it makes an ideal place for bacteria to grow. This is why most people with CF eventually have lung infections.
Most people with CF also have problems digesting food, and this is a big reason they may have problems with growing. The thick, sticky mucus blocks the ducts from the pancreas to the small intestine, so that the digestive enzymes from the pancreas cannot get to the small intestine to help digest food. This is called malabsorption or pancreatic insufficiency.
Download An Introduction to Cystic Fibrosis: For Patients and Their Families
The Genetics of Cystic Fibrosis
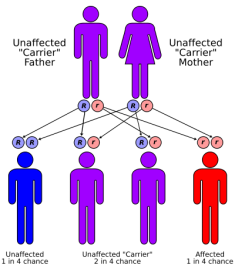
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disease. This means that CF is inherited. A child will be born with CF only if two CF genes are inherited - one from the mother and one from the father. A person who has only one CF gene is healthy and said to be a "carrier" of the disease. A carrier has an increased chance of having a child with CF. This type of inheritance is called "autosomal recessive." Autosomal means that the gene is on one of the first 22 pairs of chromosomes which do not determine gender, so that the disease equally affects males and females. "Recessive" means that two copies of the gene, one inherited from each parent, are necessary to have the condition. Once parents have had a child with CF, there is a one in four, or 25 percent, chance with each subsequent pregnancy for another child to be born with CF. This means that there is a three out of four, or 75 percent chance, for another child to not have CF.
The birth of a child with CF is often a total surprise to a family, since most of the time there is no previous family history of CF. Many autosomal recessive conditions occur this way. Since both parents are healthy, they had no prior knowledge that they carried the gene, nor that they passed the gene to the pregnancy at the same time.
Genes are founds on structures in the cells of our body called "chromosomes." There are normally 46 total, or 23 pairs of chromosomes in each cell of our body. The seventh pair of chromosomes contains a gene called the CFTR (cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator) gene. Mutations or errors in this gene are what cause CF. This gene is quite large and complex. Over 1,000 different mutations in this gene have been found which cause CF.
The risk for having a mutation in the gene for CF depends on your ethnic background (for persons without a family history of CF):
| Ethnic Background | Risk of CF Mutation | Risk of Child with CF |
| Caucasian | 1 in 29 | 1 in 3,300 |
| Ashkenazi/Jewish | 1 in 29 | 1 in 3,300 |
| Hispanic | 1 in 46 | 1 in 8,000-9,000 |
| African-American | 1 in 65 | 1 in 15,000 |
| Asian | 1 in 90 | 1 in 32,000 |
Testing for the CF gene can be done from a small blood sample or from a "cheek swab," which is a brush rubbed against the inside of your cheek to obtain cells for testing. Laboratories generally test for the most common mutations, and most labs test for anywhere from 30 to 100 total mutations. The detection rate depends on the person's ethnic background. In general, the detection rate for the Caucasian population is around 90 percent, 97 percent or more for the Ashkenazi population, 57 percent for Hispanics, 75 percent for African-Americans, and 30 percent for Asians. The detection rate differs because CF is more common in certain geographical areas and certain populations of the world. The diagnosis is confirmed by another test call the sweat chloride test.
There are many people with CF whose mutations have not been identified. In other words, all of the genetic errors that cause the disease have not been discovered. Because not all mutations are detectable, a person can still be a CF carrier even if no mutations were found by carrier testing.
Testing for the CF gene is recommended for anyone who has a family member with the disease, or whose partner is a known carrier of CF or affected with CF.
Infection Control
The Cystic Fibrosis Center abides by strict infection control guidelines both inpatient and outpatient programs. These guidelines are set forth by the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation for the protection of all people living with CF while in the medical center. The following guidelines reflect current infection control procedures in clinic, including changes made recently based on the Updated Consensus guidelines from the CF Foundation Spring, 2014.
Information on Germs and Lung Health Information on Stopping the Spread of Germs
Outpatient Center
- Contact between CF patients needs to be very limited. People with CF should stay at least six feet from each other. Every attempt is made to move patients and families quickly through registration and into a visit room.
- While in the waiting room, ALL patients will be asked to wear a mask. Masks are available at the registration desk in both the pediatric and adult clinics and should be worn any time you are outside your clinic or hospital room.
- For the pediatric program, we encourage parents to supervise children at all times and we also recommend that children bring their own toys from home rather than playing the with toys in the waiting room.
- We discourage use of the computer in the waiting room for infection control reasons.
- All staff will gown and glove for your visits. This will include all front end nursing staff and the CF team.
- Staff wash their hands on the way into and out of each patient’s room.
- The respiratory therapist will gown, glove and mask while assisting patients with PFTs as well as when collecting sputum samples.
- Patients are also strongly encouraged to stay in the treatment room at all times unless using the bathroom.
- All treatment rooms, triage areas and equipment is wiped down with anti-bacterial wipes after each patient. These wipes are approved for all bacteria, including Pseudomonas and B. Cepacia.
- MRSA Precautions: Current guidelines require that all patients be placed on contact precautions, Previously, this policy was only for patients colonized with MRSA.
- Pulmonary function testing and sputum cultures will take place in your clinic room rather than moving in and our of the pft lab. The purpose of this is to reduce exposure to bacteria that may remain airborne for up to 30 minutes after testing. If the pft lab is used for any testing, the RT will clean the room and allow 30 minutes between patients.
- Patients will be asked to wear gloves while performing pulmonary function testing.
Note: CF related MRSA is NOT a danger to people in the community.
**B. Cepacia: Patients who culture Burkholdeia cepacia will continue to be scheduled to come to clinic on a different day than the primary CF clinic day. Currently, these are the second and fifth Friday of every month in the pediatric program and one Thursday per month in the adult program. Similar infection control policies will be in place on B. Cepacia clinic days.
Hospital Infection Control Policy
All pediatric, adolescent and adult patients with CF will be placed on contact precautions during their stay at BMSCH and RWJUH. This means the following:
- All patients with Cystic Fibrosis will always be in a private room.
- All hospital staff must gown and glove when entering the room and remove gown and glove and wash hands upon leaving the room. This includes doctors, residents, nurses, assistants and housekeeping staff.
- All patients with CF should have their own stethoscope and blood pressure cuff in their room. If you do not, please ask your nurse or medical technician.
- All patients must wear a mask when leaving the room and will not be allowed to visit another patient with CF in the hospital.
- Patients who wish to leave their rooms must wear a mask and are strongly encouraged to go for walks off the unit.
- Doors to patient rooms should remain closed
- Respiratory therapists must wear masks in addition to gown and glove because they are inducing sputum.
- Whenever possible, CF patients will perform pfts in their hospital rooms rather than coming down to the pft lab.
- No two CF patients will be assigned to the same nurse on a given day
- Family visitors are not limited. However, family members who are sick are discouraged from visiting.
- Pediatric and adolescent patients are not allowed in the Child Life room or Teen lounge. Representatives from the Child Life Department will visit patients frequently and bring various activities, games, etc to rooms.
Creating a Medical Profile
Cystic Fibrosis can be a very demanding disease to manage and there is a lot to remember! Often in CF, children and adults get involved with doctors from various disciplines, like Gastroenterology or Endocrinology. Keeping track of medications, changes, appointments and events in your medical history can challenge even those of us with the best memory and organizational skills. You are also asked similar questions time and time again, resulting in the need to repeat yourself.
Many families have found that keeping a medical profile can be very helpful in keeping track of everything. It can also be very helpful to your medical providers to review it for any changes, new medications, etc. Medical profiles will also save you tremendous time when asked to recite all of your child's medications, medical history, etc.
We recommend you develop a medical profile and carry it with you to appointments, procedures, hospitalizations, etc. There are so many ways to do this and so many formats that people find helpful. Attached is one format that some of our families use. Feel free to print this or download it and use it.
Overview
According to the CF Foundation, there are many things you can do to prevent illness and keep your lungs healthy.
Most people with cystic fibrosis can lead active lives with routine therapies and regular visits to a Cystic Fibrosis Foundation-accredited care center.
Knowing your CF is important to staying healthy. The staff at our center partner with you to develop individual treatment plans. These plans typically include high-calorie, high-fat diets, therapies to loosen the clogged mucus from the airways, and mucus-thinning drugs and antibiotics when needed.
By following a treatment plan developed your CF team, you can slow down the progression of the disease. A healthier body is better able to deal with bacteria and chronic lung infection.
Avoiding the Spread of Germs
Cystic fibrosis puts the airways at risk for lung infections. There are, however, effective ways to lessen the risk. One way is to limit contact with known germ sources.
Although germs are everywhere and cannot be avoided, one of the best ways to keep from catching or spreading germs is through effective hand-washing, whether with soap and water or alcohol-based hand gels.
Everyone with CF should avoid unnecessary contact with people who have a cold or any other contagious illness, and should cough and sneeze into a tissue.
Get the Flu Shot
Flu season, which begins in August and lasts throughout the winter, is the time of year that the influenza virus is easiest to catch. The flu is considered highly contagious, because it can spread by direct contact, coughing, sneezing, and when an infected person touches a surface that others then use, like door knobs and railings.
People with lung infections, including people with CF, can develop more serious cases of the flu, so it is important for you to get a flu shot to be immunized against the most prevalent strains.
Our care center offers the flu shot to all patients with CF beginning in August every year.
Everyone with CF and members of their households who are at least 6 months old need to be vaccinated for both viruses.
Staying Hydrated During the Summer
When summer comes, we want to work with you to make sure you have a healthy and happy summer. Here are some tips on staying healthy in the hot months!
- HYDRATE, HYDRATE, HYDRATE - Remember, people with CF can lose up to 5 times more salt in their sweat than someone without CF. Remember to drink even when you are not thirsty, especially during outdoor exercise. Drink before, during and after exercise. Sports drinks with added salt and carbohydrates are great at this time of year. Children are more susceptible to dehydration to make sure the little ones drink extra!
- Caffeine does NOT count as part of the total ounces of liquid you drink in a day. This includes all caffeinated sodas, coffees and tea.
- Infants dehydrate more quickly than young children and adults so keep your baby well hydrated and in cool clothing.
- EAT MORE SALT!! - Examples of foods to add during the summer are: pretzels, salted nurs and seeds.
- Know the signs of dehydration and hypoatremia (low sodium levels in your blood). These might include nausea, vomitting, headaches, muscle weakness and cramping. Call your CF team with any concerns.
- Medications - Keep your medications cool while out and about. Some medications require refrigeration so make sure you know which of your meds need to be in the fridge. Others, like enzymes, should be kept at room temperature. Keep a cooler handy if you are going out and plan to bring your enzymes or other medications..
- Wear your sunscreen!! SPF should be 30.
Secondhand Smoke

The Dangers Of Secondhand Smoke
Your cystic fibrosis care center is concerned about second hand smoke and its effects on the lungs. All world health groups agree that second hand smoke can cause serious problems to people with normal lungs. People with CF are even more at risk.
Respiratory Treatments
Accordion Content
Understanding how these medications work and why you take them in specific order will help you appreciate the importance of timing. Since CF care is individualized, some people may not be prescribed all the medications listed, in which case you just follow the order leaving out the medications that are not prescribed for you.
-
Example: Albuterol, ProAir, Ventolin, Proventil)
A bronchodilator relaxes the smooth muscle of the airways, opening them up and allowing for better airflow and easier airway clearance. -
(Example: Hypertonic Saline)
Inhalation of a 7% hypertonic saline solutions (HTS) aids in hydrating the thick mucus making it easier to move. Since HTS can cause bronchospasm, it is recommended that a bronchodilator always be given first. -
(Example: Pulmozyme, Mucomyst)
Mucolytics thin the thick, sticky mucus in the lungs. When the mucus is less think and sticky it is easier to mobilize and cough or huff out. -
(Example: CPT, Vest, acapella, huffing, PEP)
Once the airways are relaxed and more open, and the mucolytic has thinned the mucus, then it is time for an airway clearance technique (ACT). An ACT will help to mobilize the mucus out of the smaller airways and into the larger ones where a cough or huff will remove it. Commonly in CF, the mucus in the lungs have millions of bacteria, so getting out as much of it out as routine, it is OK to do steps 1,2,3 in that order while you are on the vest or receiving CPTTypical vest treatments should take 20-30 minutes. Your vest settings may need to be adjusted over time as will your vest size. We typically begin to fit children for vests around age 2 and vest size will change frequently into adulthood. Most insurance companies now cover vests for all patients without difficulty and vest companies will work with you with any difficulties you have, including repairs, upgrades, etc.
-
(Example: Tobi, Tobi podhaler, Colistin, Cayston)
After your airway clearance and cough or huff maneuver has cleared your lungs of the loosened mucus, it is time for the inhaled antibiotic, which helps to kill the bacteria remaining in the lungs. -
Example: Flovent, Advair)
CF airways can become inflamed from all the mucus and infection. Anti-inflammatory medication will help reduce this swelling. It is best to take this last, after all of the other medications are taken. Always remember to rinse you mouth after inhaled steroids.
Additional Resources
Please ask the CF team any questions you may have.
Tips for Good Therapy
Accordion Content
Understanding how these medications work and why you take them in specific order will help you appreciate the importance of timing. Since CF care is individualized, some people may not be prescribed all the medications listed, in which case you just follow the order leaving out the medications that are not prescribed for you.
-
- Read stories and cuddle during neb and treatment time
- Blow bubbles
- Sing songs
- Be goofy
- Bounce on a exercise ball gently with child on lap
- Infants - Use exercise ball and gently bounce and stretch babies arms and legs, clap and laugh on it while singing to your baby (ABCs work), tickle the baby
- Chase them on your hands and knees, be animals, growl
- Party blowers
- 9-24 months- mini- trampoline for 10 minutes holding his hands babies love to bounce
- Make him/her laugh till they cough (Tickle me Elmo)
Always do nebulizer treatment before the 20 minutes of play, chase, or ball. Encourage the other siblings to participate. Substitute 1 fun family therapy – jumping, swimming - and skip the real one once a week as a reward.
-
All the above and add in once or twice a week, or as a reward
- Exercise ball and bounce laugh sing Humm (20 min)
- Humming is a great lead in to the Huff coughpic2
- Blow toys (party blower)
- Roll inflated toys, play crawling games, hide and seek
- Mini trampoline with assistance
- Bubble pep
-
- Family Swim; 30 minutes playing in the water
- Water slide, kick the width with a kickboard, race each otherv
- Kickball with the family and friends
- One legged races, hop till you drop
- Skip and sing
- Exercise ball
- Hand PD – just for a change
- Mini trampoline, trampoline
- Square Dance, ZUMBA, Roller skate or blades
- Spinning
- Biking, Hiking
- Common sense should always prevail. Do the neb treatment first, develop healthy habits and encourage your child or yourself.
Exercise
In addition to respiratory therapies and oral medications, exercise has been found to be extremely beneficial to people living with CF at all ages. We cannot underestimate the importance of adding this to you/your child's routines. Patients report a much greater feeling of well being when involved in a regular exercise routine.
Signs of Illness
When to Call the Cystic Fibrosis Center
Your/your child's health is our primary concern. We are available to assist you in maintaining your health and prescribing treatment when necessary. There is always someone on call to help at any time of day or night. Here are some things to look for that may require a call to the CF center:
- Increased respiratory symptoms such as: increased cough and/or sputum production, chest tightness, shortness of breath, increased congestion, wheezing, nighttime awakening due to cough
- Increased fatigue, fever, lethargy, weight loss, change in appetite
- Symptoms of dehydration, including excessive thirst, lack of tears, increased sweating, dry mouth, dry diaper, decreased urination, lethargy
- Any signs of hemoptysis (spitting of blood). Be prepared to describe color, amount and when it started,( ie. streaking, size of a coin, tablespoon, shot glass)
- Change in bowel habits, i.e. constipation, diarrhea, loose or greasy stools, blood in stool, nausea, vomiting
- Abdominal pain, moderate to severe, abdominal distention, bloating, gas, vomiting
- Unexplained fatigue, increased urination or thirst
Overview
In this section, you will learn about the most common tests ordered for CF patients.
At diagnosis, we perform several tests to help us make the diagnosis and determine what treatment you will require.
After diagnosis, we ask all CF patients to have annual studies. Annual studies are a critical part of your ongoing care and are strongly recommended by the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation. They are an important tool we use to help you monitor your (your child's) health, nutrition status and the progress of your lung disease. Our goal is to help you (your child) remain as healthy as possible.
Routine testing is also done at every clinic visit. This includes pulmonary function testing and sputum cultures.
Bronchoscopy is also described in this section.
If you have any questions about the tests we perform, please feel free to discuss with the team.
Sweat Testing
Accordion Content
If a person shows symptoms of CF or if a baby has a positive newborn screen for CF, a doctor may order a sweat test. This simple, painless test is the best way to diagnose CF. It measures the concentration of salt in a person’s sweat. A high salt level indicates CF.
Sweat tests should be done at a Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Accredited Care Center where strict guidelines help ensure accurate results.
-
The sweat test has been the “gold standard” for diagnosing cystic fibrosis (CF) for more than 40 years. When it is performed by trained technicians, and evaluated in an experienced, reliable laboratory, the sweat test is still the best test to diagnose CF. It is recommended that the sweat test be performed in a Cystic Fibrosis Foundation-accredited care center where strict guidelines are followed to ensure the accuracy of the results. The test can be performed on individuals of any age. However, some infants may not make enough sweat for the laboratory to analyze. If an infant does not produce enough sweat on the first sweat test, it should be repeated to collect more.
-
The sweat test determines the amount of chloride in the sweat. There are no needles involved in the procedure. In the first part of the test, a colorless, odorless chemical, known to cause sweating, is applied to a small area on an arm or leg. An electrode is then attached to the arm or leg, which allows the technician to apply a weak electrical current to the area to stimulate sweating. Individuals may feel a tingling sensation in the area, or a feeling of warmth. This part of the procedure lasts approximately five minutes. The second part of the test consists of cleaning the stimulated area and collecting the sweat on a piece of filter paper or gauze or in a plastic coil. Thirty minutes later, the collected sweat is sent to a hospital laboratory for analysis. The entire collection procedure takes approximately one hour.
-
Your physician has asked that this test be performed to rule out the presence of CF, an inherited disorder of the lungs, intestines and sweat glands. Most children and adults with CF have an increased amount of chloride (salt) in their sweat. In general, sweat chloride concentrations less than 40 mmol/L are normal (does not have CF); values between 40 to 60 mmol/L are borderline, and sweat chloride concentrations greater than 60 mmol/L are consistent with the diagnosis of CF. For infants under 1 year of age, sweat chloride concentrations less than 30 are considered normal. For individuals who have CF, the sweat chloride test is most often positive from birth. Once a test result is positive, it is always positive. Sweat test values for people with CF do not change from positive to negative or negative to positive, as a person grows older. Sweat test values also do not vary when individuals have colds or other temporary illnesses.
A negative sweat test does not rule out the possibility of Cystic Fibrosis. There are some mutations that may result in a normal sweat value but the person still has clinical signs and symptoms of Cystic Fibrosis.
-
There are no restrictions on activity or diet or special preparations before the test. However, one should not apply creams or lotions to the skin 24 hours before the test. All regular medications may be continued and will have no effect on the test results.
Generally, we recommend you bring extra clothing and blankets to warm your child so he/she will sweat more easily.
-
Sweat test results are usually available in our physician's office the same day as the test was performed and can be provided to your physician on the next working day after the test is performed. In a small number of cases, the quantity of sweat obtained is not sufficient to give an accurate result, and the test may need to be repeated.
-
Yes. In a small number of cases, the test results fall into "negative" or “borderline” range between not having CF and indicative of CF. In these situations, repeat sweat tests, as well as other diagnostic procedures, may need to be carried out. These will only be done after consultation with a physician.
For more information about the CF Foundation and the programs and services available to people with the disease, or to learn how you can volunteer and help make a difference, please visit the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation or call (800) FIGHT CF.
Genetic Mutation
Newborn Screening
Newborns screened for cystic fibrosis can benefit from early diagnosis and treatment, which can:
- Improve growth;
- Help keep lungs healthy;
- Reduce hospital stays; and
- Add years to life
While newborn screening is not a definitive diagnostic test for cystic fibrosis, it may lead to tests that can rule out or confirm a CF diagnosis. All states in the U.S. screen newborns for cystic fibrosis.
In New Jersey, all newborns are screened with 1-2 days after birth. Results of the newborn screen will be sent directly to your pediatrician along with recommendations for repeat or referral if screen was positive. A positive newborn screen is NOT a diagnosis of Cystic Fibrosis. Usually the screen is repeated and if the second screen is also positive, you and your child should be referred to an accredited CF Center for further testing.
Genetic Testing
When a patient is referred to our center for testing, we may order a few genetic tests to look for the presence of two CF causing mutations.
Only about one of every 3,000 Caucasian newborns has CF. We know there are more than 1,800 known mutations of the gene that causes CF. However, not all mutations cause CF. The ones that do cause CF are called "disease-causing" mutations. Current tests look for the most common disease-causing mutations.
More than 10 million Americans are carriers of one mutation of the CF gene. Among Caucasian Americans, about one in 29 people carry one mutation of the CF gene. In other races or ethnicities, one in 46 Hispanic Americans, one in 65 African Americans and one in 90 Asian Americans carry a mutation of the CF gene.
People inherit (or get) genes from their parents. To have CF, a child must inherit one copy of a mutation of the CF gene from each parent. In other words, the child must have two copies of the gene with mutations to have CF. Both males and females can have the disease.
People who have only one copy of the CF gene do not have. They are called "carriers" of the CF gene.
The chances of being a carrier of one CF mutation or having CF (with two CF disease-causing mutations) depend on your race and ethnicity. CF gene mutations are most common in Caucasian Americans (white people whose ancestors or family are from Europe).
In the U.S., the number of people who carry a CF gene is about:
- 1 in 29 Caucasian Americans;
- 1 in 46 Hispanic Americans;
- 1 in 65 African Americans; and
- 1 in 90 Asian Americans.
In the U.S., the number of people who have CF is about:
- 1 in 2,500–3,500 Caucasian Americans;
- 1 in 4,000–10,000 Hispanic Americans;
- 1 in 15,000–20,000 African Americans; and
- 1 in 100,000 Asian Americans.
Pancreatic Function
According to the CF Foundation, the pancreas is a gland in the body connected to the small intestine. The small intestine is where most of the digestion and absorption of food occurs. One of the functions of the pancreas is to make enzymes that digest food. Digestive enzymes from the pancreas enter the small intestine through a small duct, or passageway. In cystic Fibrosis, the ducts int he pancreas become clogged with thick, sticky mucous. The mucous blocks the enzymes from reaching food in the small intestine. This can lead to poor digestion and absorption of food, as well as problems with weight gain. Fortunately, pancreatic enzyme replacements or "enzymes" are available to help people with CF digest and absorb their food.
Signs of Maldigestion and Malabsorption:
- Poor weight gain despite a good (sometimes ravenous) appetite;
- Frequent, loose and/or large bowel movements;
- Foul-smelling bowel movements;
- Mucus or oil in the bowel movement;
- Excessive gas and/or stomach pain;
- Distention or bloating.
Just under 90% of patients with CF are pancreatic insufficient (PI) and require life-long supplementation with pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT). Fecal elastase is an enzyme- linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) that can be performed on a single stool sample to define pancreatic functional status. Your physician will order a Pancreatic Fecal Elastase to be performed at most local laboratories. The result of this test will tell us if your/your child's pancreas is functioning well enough or if there is a need for enzymes.
Persons with CF who have not yet started taking enzymes may have any or all of the symptoms listed above. Improvement is generally noted once enzymes are started. Sometimes, people with CF who already take enzymes experience these symptoms. This may suggest that the dose or type of enzymes may need to be adjusted. Do not increase or decrease the dose of enzymes without talking to your CF dietitian or care provider. Always give the prescribed dose of enzymes.
Sputum Culture
Per CF Foundation Guidelines, sputum cultures are obtained at every clinic and hospitalization to see what bacteria you may have and what antibiotics can be effective in fighting it. The CFF consensus statement on infection control now recommends quarterly sputum cultures and cultures during acute exacerbations. Children and adults who cannot produce a sputum sample will receive a throat swab. However, a sputum sample is preferred once a child is old enough to produce sputum.
The Robert Wood Johnson University Hospital microbiology laboratory meets the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation’s (CFF) standards of care for processing CF sputum cultures. The CFF established standards for processing CF sputum require that CF sputum must be plated within 3 hours on specific media to obtain accurate results. Inaccurate sputum culture results can impact treatment decisions and health outcomes
There will be times when we might also choose to run a "fungal culture" or AFB (Acid Fast Bacilli) test for other bacteria that may be causing illness. These tests can only be run on sputum samples, rather than a "throat swab". Below is a list of terms used to describe sensitivity testing done for the bacteria grown in your culture.
Accordion Content
-
Means that the bacteria are still “sensitive” to the effects of antibiotics and therefore can be killed or weakened by them.
-
Means that the bacteria is between sensitive and resistant to the effects of antibiotics and the antibiotics may no longer be effective in killing the bacteria.
-
Means that the bacteria are “resistant” to the effects of antibiotics. When bacteria are resistant, they are no longer killed or weakened by the antibiotics. The bacteria are considered resistant, when at least one major class of antibiotics is no longer effective in killing the bacteria.
-
Means that the bacteria are resistant to at least two major classes of antibiotics.
-
Where the bacteria are resistant to all the major classes of antibiotics.
Your physician will use information from your sputum culture along with other clinical symptoms to determine whether or not you need antibiotic treatment at that time and what treatment would be most effective.
Bronchoscopy
There may be times when the doctor believes there is a need for a bronchoscopy. This is often suggested when patients are not responding to therapy as well as expected, are getting sick more frequently, or the doctor suspects there is unidentified bacteria in the lungs which needs treatment. During a bronchoscopy, the doctor can obtain sputum cultures from deeper sections of the lungs for testing. The doctor also has an opportunity to clear mucous plugs from the lungs during the procedure.
Is a minimally invasive procedure done under general anesthesia with a flexible bronchoscope. After obtaining consent from a parent or guardian, the patient is placed under general anesthesia by our pediatric anesthesia team. Bronchoscopy is performed through an airway provided by our anesthesia team, both lungs are examined and limited washings for cultures are performed and samples are combined and sent for testing.
Culture results from the bronchoscopy are sometimes immediately available but some cultures will grow for up to six weeks before they are finalized.
Annual Studies
Accordion Content
Per recommendations of the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation the following studies are recommended to be done annually. Any questions please speak with your CF Team member.
-
To check blood counts, electrolytes, liver function, clotting times, fat soluble vitamin levels, liver function, lipid panel, immunoglobulins
-
All patients ten years and older are recommended to have an oral glucose tolerance test once annually to screen for CF Related Diabetes. This is usually done at the time of annual studies and can be done the same day as all other annual bloodwork.
The test takes 2-3 hours to complete. Blood glucose levels are taken in fasting state, one hour and two hours after glucola. We also obtain a Hemoglobin A1C, which indicates what your average glucose control has been for the past three months.
Pediatric and adolescent patients will usually be scheduled to have blood work and oral glucose tolerance test at the Same Day Surgery at Bristol-Myers Squibb Children’s Hospital at RWJUH. The CF team work with you to arrange arrange the admission and our prior authorization department will work with your insurance carrier to get approval for payment prior to the day of testing.
-
RWJ’s X-Rays now are done at 10 Plum Street office (732-249-4410). If done at hospital other than RWJ, please ask for CD and bring that and report to next clinic appt.
Pediatric patients coming to Same Day Surgery will have Chest X-Ray during same visit.
-
To do complete lung function evaluation.
*Do not take bronchodilator prior to test.
Pediatric patients coming to Same Day Surgery will PFT’s scheduled on same day.
-
To check bone mineral density/ presence of osteopenia or osteoporosis
This test is done anywhere between 1 and five years apart, depending on the results. Normal dexa scans do not need to be repeated for five years. Abnormal will require treatment and will be repeated within 1-2 years.
Diagnosis
When you or your child is diagnosed with Cystic Fibrosis, you, like many others, may know very little about this illness. Diagnosis may come as a shock and can be a very difficult thing to face. Diagnosis also leads to many questions and may result in feelings of being overwhelmed, fear, anxiety and sadness. As your CF care team, we are committed to helping you and your family adjust to the diagnosis, develop skills and knowledge to manage the illness, and find a balance between taking care of CF and living a normal life. It is critical for parents to help their children develop normally and have the same expectations of their child as parents do for children who do not have Cystic Fibrosis. This will give your child the best quality of life and help them to prepare for adulthood.
Your CF team will give you books developed by the Family Education program of the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation. These books will help to address most areas of concern and provide a great deal of knowledge about treatments and healthy living with CF. It is also important to note that patients and families become part of the care team. We want you to be a partner in your/your child's care.
In this section, you will hear from other families about their experiences living with CF. You will also be able to get more insight into the various areas that are impacted by Cystic Fibrosis, including education and employment.
Adjusting to Diagnosis

This is a common diagnosis story sent in by a family at our CF Center.
It was a Friday evening at approximately 4:45pm. The telephone rang and I headed to my phone in the kitchen. I answered the phone and the caller on the other end of the line identified herself as the receptionist from my 9-day old newborn’s pediatrician’s office. The receptionist said, “The results from your newborn’s screening just arrived and it is presumptive positive for Cystic Fibrosis, can you please hold?” As I stood holding the phone receiver in my hand, I immediately felt numb and confused. Being a new mom and young, I had no idea of what Cystic Fibrosis is (I was barely able to say it in my head), but knew it did not sound good. After what felt like an eternity had passed, the receptionist came back on the line and said, “The doctor would like to see you on Monday to discuss the results and schedule a test to confirm the results.” An appointment was scheduled for Monday and the phone call ended. I stood there for a moment trying to process what was just told to me. I tried to call the office back to see if the doctor was available so I could ask “What is Cystic Fibrosis?” However, being that it was two minutes until five o’clock on a Friday evening, no one would answer the phone. I quickly glimpsed at my newborn, who was peacefully asleep on the couch. I immediately logged onto my computer, went to a search engine and typed Cystic Fibrosis. I could feel my heart pounding as I waited for the webpage to load. I clicked on the first site that popped up and started reading. My eyes were flying over the words and seeing words like, Life-Threatening, median age, skin salty to taste. The last one caught my eye, “skin salty to taste”. I got up and ran through my apartment to my baby. I licked her forehead only to find that it had a light salt taste; I licked my arm as a comparison. I knew right then that the words on my computer screen were true and did not need a medical test to confirm my thoughts. I began to cry which turned into weeping as I went back to my computer and kept reading. Upon my husband returning home, I was crying so uncontrollably that I was barely able to speak. All I could say between sobs was, “She has Cystic Fibrosis.”
The following week involved driving to the local Cystic Fibrosis Center and having our newborn go through the Sweat Test Screening. We waited at the hospital for the test to be run. As we ate lunch in the hospital cafeteria, I kept looking at my new baby girl thinking she looks okay and that there is nothing wrong with her. Some of the information on the website mentioned problems that some infants have with regaining their birth weight. I knew in the back of my head that since we left the hospital 15 days ago she had no problems regaining her weight. So, I had a small hope that I was worrying too much as I always do and there was nothing wrong after all. We finished lunch and had another short wait before being lead into the exam room. My husband and I sat in the room in silence while our newborn slept in the car carrier. The doctor entered the room with the nurse practitioner and delivered the news that our daughter in fact has Cystic Fibrosis. As the doctor talked and gave general information about Cystic Fibrosis I half-listened. I had so many thoughts running through my head like, “What does this mean? Is she going to die? What do I now?” The doctor handed us prescription after prescription saying, “This is for this, this is for that”. I tried to take notes, but it was all so confusing. I left that appointment feeling scared, confused and sad; but most of all I was determined to learn as much as I could.
You may or may not find similarities in my recollection of how we learned of our daughter’s disease. However, one thing is certain for all of us, we all have a story of how we began on the CF journey. A journey that is constantly changing and unique for each person.
Whether you are the parent (or any relative) of a child newly diagnosed or you yourself have been diagnosed, either situation brings on more questions/concerns than answers. You will go through many mixed emotions and may feel overwhelmed with this diagnosis.
The best advice that I, as a parent of a child with CF, would give to others on this journey would be to take one day at a time. You are NOT going to understand everything overnight. While you are adjusting to the diagnosis, try to get into a “routine” of giving/taking meds as soon as possible. The sooner you establish a “routine”, the better for the health of your child/self.
As a non-medical person, I would suggest the following:
- Read, Read, Read – Educate yourself about this disease to best of your ability.
- Ask Questions – Do not be afraid to ask your CF team any question (hopefully this guide will answer some of your questions).
- Get Support - Surround yourself with support from others that are going through the same experiences and/or seek assistance from family and friends.
In the end, if you still feel that the diagnosis is too much for you to handle on your own I would recommend seeking professional help.
Creating a Support System and Moving Forward
It is important to note that CF is a chronic disease and you/your child will live with this for your entire life. You will be asked to learn about various treatments and medications that you/your child requires daily. These treatments are intended to slow the progression of the disease and keep you/your child healthy. These treatments typicallly include airway clearance, nebulizer treatments, pancreatic enzymes, CF specific vitamins and oral antibiotics. We strongly encourage you to think about taking some of these steps to help with the adjustment:
- Make CF treatments part of your daily routine
- Share responsibilities with your partner/family member
- Find people to talk to, develop a support system
- Expect letdowns, do not expect this to be a smooth road
- Take time for yourself and do things you enjoy
Once you have made the initial adjustment to CF, you will start looking forward and planning ahead. As you and your family move through life, here are some age specific resources that might be helpful.
Family Centered Care
The Cystic Fibrosis Center is committed to patient and family centered care. Our pediatric and adult teams work closely with one another and with our families to make sure that the care in clinic and in the hospital is always improving to meet your needs. In order to assure that we remained focused on empowering patients and families and providing sensitive and wholistic care, we have implemented several programs:
Family Advisory Council
This council is central to our efforts to remain patient and family centered and is comprised of family members from both the pediatric and adult programs as well as staff from both programs. The council meets several times per year and is involved in planning new outreach programs for families, communication strategies, family education day, etc. This group is also instrumental in providing feedback about the quality of care in clinic and in the hospital. Membership on this council is always open and we welcome new ideas. Members can participate in person or via conference call. In the last year, the council has focused on several priorities:
-
Family Resource Website - This guide, originally envisioned as a book to give to patients and families, has expanded to the development of an entire website dedicated to our CF center and families. This is a comprehensive guide to our CF center and the hospital, both pediatric and adult. The most important aspect of this project is that families have been involved in the development from the beginning and are an integral part of the project.
-
Center Newsletter/EBlast - This Eblast is managed entirely by the Family Advisory Council with contributions from the staff at both programs. The first edition of the newsletter was released in May 2012. The purpose is to keep families involved in the center and up to date on anything new in the CF community.
-
Family to Family Support Network - This is an informal network at this time which provides support to families of CF patients at challenging times in their lives. Matches are made by the center staff and only with permission from both parties. The staff at the center has already paired family members or patients within the center who express a need for additional support.
-
EPal program - This program was launched in early spring, 2012. The intent of this program is to give our patients and siblings someone “like them” to talk to, with the approval and supervision of their parents. The center staff assist in making the connection but has no involvement in the relationship beyond that point.
The CF center has also developed a patient satisfaction survey. Information from the survey is used to improve care.
The social worker regularly uses an email network with willing families to keep you updated quickly on changes, new information, etc. This email network has made communication much easier and has helped families feel more connected to their center and new information that comes from the foundation and other sources.
In 2013, the CF team started our own CF walk in New Brunswick with the help of the NJ Chapter of the CF Foundation. This was the first walk for the New Brunswick location and raised over $30,000 in its first year. In its second year, the walk moved to Edison and raised $52,000. We hope this walk will grow with every passing year and will include as many families from this center as possible.
The CF Center holds Family Education Day once per year. All the members of the CF team from both the pediatric and adult program attend the meeting. This day is usually full of updates for families on activities at our center as well as research and other programs sponsored by the CF Foundation. We always welcome a keynote speaker and the afternoon is full of small group discussions, where family members get the chance to meet one another and talk about life with CF. Many families find this a rewarding part of the day.
Education
We strongly encourage you to plan with your child to have a long and full life. Education is part of that. Children with CF can participate in all the activities that children without CF can participate in. They should be encouraged to work hard in school and plan for their future. However, there may be times when having CF interferes with their daily routine or their ability to meet all expectations. Children and adults with CF also have special needs that we need to prioritize in order to keep them healthy in school and give them the best chance of success.
To that end, we usually encourage all families to work with their schools to establish an appropriate 504 plan or IEP if needed. This is often something that you initiate when your child begins Kindergarten but can be initiated at any time over the years they are in school.
When students get to college and post graduate education levels, schools have fewer guidelines that they must follow and the rules change but you are still eligible for certain accommodations and services. Registering with the Office For Disabilities at the university or college your are enrolled in should be a first step. Accommodations for residency are very common and your CF center social worker will assist you with this.
You will find links below to helpful information about school and CF, as well as stories from our families about common issues they have dealth with in school. For those in college, there is also information on going away to school and what to think about. The social worker at our center can assist you with any of your school related needs.
Adulthood and Cystic Fibrosis
People with CF are now living full lives well into adulthood. Our patients have careers and families and work hard every day to stay well. Young adults transition to the adult CF program by age 23 or before. The adult program works hard to provide the same level of care that patients have grown up with in their pediatric centers. However, adulthood brings different challenges and adventures and the adult team pays close attention to those issues. The major decisions and events that adults with CF face are career, marriage, families, future planning and planning for their healthcare.
Pretty soon, over half of the population living with CF will be over 18. The CF Foundation and adult CF programs around the country are working hard to address the special needs of adults. Below are some links to more information:
Information on Managing Cystic Fibrosis
It is important to remember, whether you have a newly diagnosed infant or you are a young adult graduating from high school, you can have a full life.
CF will present you or your adult child with challenges and hurdles but there will be a lot of support along the way. Be open to the possibilities and you will achieve much more than you might think.
Insurance
Health insurance and health care costs can be very intimidating. Health insurance has become very complex in today's world and it can sometimes feel like your health insurance gets in the way of good health care! As a parent of someone living with CF or an adult who is living with CF, it is very important that you understand your benefit plan and stay on top of the changes that often happen in a plan on an annual basis. The social worker at your CF center would be happy to help you understand and navigate this universe if things get complicated. Our office also has a department for prior authorizations that helps to get things approved when needed, whether that is an expensive test or a medication that might requires approval. Please feel free to call our office when you have questions.
The recent health care legislation and addition of Obamacare has helped people with CF in many ways but has also complicated things. If you have questions about the healthcare legislation or Obamacare, visit HealthCare.gov.
Below is also a helpful breakdown of the changes that came with the new healthcare legislation. If you believe you might qualify for NJ Family Care or medicaid, this is also a good site to go to for information. You can also visit www.njfamilycare.org.
In some cases, you may find yourself without health insurance and not knowing what to do. Please be assured that we are here to help guide you through this and can help you get many of your medications. Please call the center social worker if you need help.
The CF Foundation has also established a patient resource center that might be very helpful for those who find themselves in difficult situations with health insurance.
Below are two more helpful documents developed by the CF Foundation to help navigate the world of health insurance.
Know Your Health Insurance Coverage Working With Your CF Center and Insurance Company
Overview
Good nutrition plays a vital role in the health of a person with Cystic Fibrosis. This cannot be underestimated or understated. Nutrition care is an important focus of attention in CF care and your dietician will meet with you regularly throughout the year to make sure you/your child are reaching and maintaining your nutrition goals. These include height and weight but also vitamin levels. Years of research through the CF patient registry has shown the following:
- Maintaining normal growth and weight that is average or above average is associated with better lung function, less frequent infections and hospitalizations in people with CF.
- Monitoring nutrition and growth is very important in CF because, as a group, infants, children, adolescents and adults with CF have heights and weights that are below average for their age and sex.
- Poor growth and lower than average weight are both correlated with decreased lung function in people with CF.
Impact of CF on Nutrition
- Chronic lung inflammation increases calorie and protein needs so children and adults with CF need more calories than a child without CF
- Appetite and food intake are often affected by illness so treating infections early can help keep appetite and weight stable. Decreased appetite and weight loss can also be a sign of illness
- CF can cause a number of gastrointestinal issues which could results in loss of nutrients due to poor absorption, vomiting, and or discomfort associated with eating
- Endocrine problems associated with CF cause abnormal metabolism (processing) of nutrients
- Social and psychological issues can affect nutritional status in any age group
Needs and Goals
Meeting Nutritional Needs and Goals
Infants, children and adolescents with CF are expected to gain weight and grow like their peers without CF.
- Your child’s weight and length are measured and monitored closely by your CF team using GROWTH CHARTS
- Length and height should progress at a predictable rate for age, sex and genetic potential.
- Weight should be maintained at an average weight for length or height according to National
Standards for all healthy children
- From birth to age 2 years weight and length are plotted on the growth chart.
A weight for length at or above the 50th percentile is an “ideal body weight” for an infant or young child with CF
- From age 2 to 20 years the body mass index (BMI) is plotted on the growth chart
BMI is the relationship between weight and height (BMI= kg body weight/m2 height)
A BMI at or above the 50th percentile is an “ideal body weight” for a child with CF.
- Adults with CF over the age of 20 are expected to maintain an average BMI
Adults with CF over the age of 20 are expected to maintain an average BMI
A Male’s ideal BMI is 23kg/ m2
Critical Growth Periods are times of life when energy and nutrient needs are at their highest and can be challenging times for maintaining optimal nutrition for people with CF
Accordion Content
-
- A time of rapid growth of bones, body tissues such as muscles, lungs, brain and other vital organs
- Growth during the first few years of life affects lung function later in life (LINK)
- Behavioral feeding issues
-
- A time of rapid growth of bones and increasing fat and or muscle mass
- A time with a higher risk for CF related diabetes (CFRD)
- Often a time of increased physical activity with organized sports
- A time of increased independence including changes is self perception, lifestyle habits, and decreased adherence to CF therapies and dips in self esteem.
-
- A time of increased energy needs to support fetal growth and development
- A time of increased nutrient needs such as iron, folic acid, essential fatty acids, calcium and vitamin D.
- A time of increased risk of abnormal glucose tolerance (insulin resistance) and gestational diabetes
- Pre-planning for pregnancy is recommended
-
- A time of increased energy needs to produce milk (about 700 additional calories daily)
- A time of increased Vit D and calcium needs
- A time of increased fluid needs
- Lactation may not be advisable if Mom is not well nourished.
Achieving Nutrition Needs
-
Calories - People with CF have calorie requirements that are higher than people without CF. They need to consume up to twice as many calories daily
-
Protein - People with CF need 1.5 to 2 times more protein in their diets
-
Fat - Due to poor fat absorption, people with CF need 10% more fat than the average person
-
Carbohydrates - Carbs are a great source of energy and calories and do not need to be avoided, even in the setting of diabetes
-
Salt and chloride (Table salt) - All people with CF need additional salt in their diet to replace higher than normal salt losses.
-
Vitamin and mineral supplementation - People with CF and pancreatic insufficiency have difficulty absorbing fat soluble vitamins A, D, E and K. CF specific vitamins were designed to offer higher levels of vitamins and minerals that CF patients need
-
Enzyme replacement therapy - 90-95% of all CF patients have pancreatic insufficiency and will need enzyme therapy to boost absorption of fat, calories, vitamins and minerals consumed.
Meeting Calorie and Nutrient Needs
High calorie, high protein, high salt diet
- Calorie boosting starts at birth and will continue as needed throughout life
- Making meals and snacks a priority takes additional time and attention
- Oral Supplements and shakes can be an easy, healthy and convenient way to add calories to the day when you are too busy to think about making calorie dense snacks
- Parents and children benefit greatly from taking a behavioral approach to feeding young children. See social and psychological issues for more information.
- Tube Feeding is sometimes necessary in more serious cases of malnutrition or when people simply cannot meet their calorie needs orally. There are two types of tube feeding, nasogastric or gastrostomy. If this option is necessary, the team will discuss this with you at length and will involve our pediatric or adult GI specialists.
Tube Feeding
Tube feeding can be a great way to get the calories and nutrients that you or your child with cystic fibrosis need to gain and maintain a healthy weight. Explore this as an option with your CF care team. Parenteral Nutrition is nutrition given through a large vein. This is only used in more serious cases of malnutrition when a G tube is not possible. There is a greater risk of infection with parenteral nutrition but it is closely monitored.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Accordion Content
-
Pancreatic Insufficiency is a condition in which a person does not have enough enzymes and bicarbonate being delivered from the pancreas to the intestine for digestion. This causes malabsorption of nutrients, failure to gain weight and grow, weight loss, vitamin and mineral deficiency, and gastrointestinal symptoms.
Most people with CF have mal-absorption due to PI. Onset usually occurs in the first one to two years of life, often in early infancy, but can start at anytime.
Symptoms of mal-absorption
- Change in number of stools
- Large, bulky stools
- Stools may be bulky and soft
- Greasy, oily or floating stools, oil in toilet water
- Stools may smell worse than usual or normal
- Rectal prolapse
- Mal-absorption of calorie providing nutrients and poor weight gain or weight loss
- Fat ……………………..9 calories/gram
- Protein…………………4 calories/gram Complex
- Carbohydrate ………...4 calories/gram
- Results in poor weight gain, weight loss, poor growth, decreased immune function and decreased lung health
- Mal-absorption of FAT SOLUBLE VITAMIN and deficiency: Vitamin A, Vitamin D, Vitamin E, Vitamin K
- Mineral deficiencies: Calcium, Zinc, Sodium, Chloride
Tests to Diagnose PI and Mal-absorption
- 72 hr fecal fat test
- Pancreatic Fecal Elastase
Treatment of PI and Mal-absorption Pancreatic Enzyme Replacement Therapy (PERT) Pancreatic enzymes are taken with each meal, snack, breast feed, bottle , and drink that contains fat protein and or complex carbohydrate.
Antacid and acid blocking medicines can be added to make enzymes work better
Fat Soluble Vitamin Supplementation with special supplements made for mal-absorption are prescribed
Each enzyme company offers programs that provide free nutritional support and/or CF therapy supportHigh Calorie, high protein diet
Even with PERT, not all calories and nutrients from food are absorbed as expected and calories and nutrients are lost and need replacement. -
Gastroesophageal reflux is a condition in which stomach acid and partially digested food can flow back up into the esophagus. GER can cause vomiting, heartburn, and esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus). Many infants have reflux, but can outgrow it. Can occur at any age. Coughing can make reflux worse. Reflux is more likely to occur when the stomach is full and when lying down.
Symptoms of GER
- Repeated vomiting or spitting up
- Frequent burping
- Stomach aches or heartburn
- Decreased appetite or feeling full after eating only a small amount (early satiety)
- Slow or no weight gain from reluctance to eat and losing food from vomiting
- GER can lead to coughing and wheezing
- GER is worsened with constipation
Treatment of GER
- Acid blocking medication
- Medication to help the stomach empty better
- Smaller more frequent meals
- Avoid carbonated drinks
- Avoid caffeine (cola, tea, coffee, and excessive chocolate)
- Do airway clearance before eating
- Reflux precautions
- Staying upright after meals
- Prop the head of the bed 6-8 inches if GER occurs at night
- Avoid playing right after meals
-
Constipation is a condition of having infrequent stools (usually less than once daily), hard or small ball-like stools that may be hard to pass or cause stomach pain, cramps and painful gas. Constipation may occur more often in people with CF.
Causes of constipation
- Abnormal stools caused by malabsorption (large, bulky)
- Reduced motion of the muscles in the walls of the intestine
- Inadequate dietary fiber and fluid intake
- Inadequate exercise or a change in exercise
Symptoms
- Full feeling and decreased appetite
- Abdominal distention or bloating
- Excess gas and abdominal pain
- Sometimes stools can look like diarrhea. This happens when stool that is more liquid leak around a stool blockage. This often occurs as an uncontrolled stool or “accident”.
Treatment
- Adequate dietary fiber and fluid intake
- Stool softeners or laxatives
- May be needed regularly
Prevention
- Drink enough fluid, at least 4-8 cups daily
- Eat a high fiber diet
- Use fiber supplement with adequate amount of water
- Get regular exercise
-
Meconium ilues is a blockage of the intestine in a newborn caused by abnormally thick viscous meconium preventing the passage of stool expected within the first 48 hours of life. MI starts even before the baby is born and can be detected by ultrasound. MI can be resolved by using enemas to clear the blockage. If this is unsuccessful, MI can result in rupture of the small intestine, a smaller than normal large intestine (micro colon), and a surgical emergency to remove the blockage. In some cases an extensive amount of intestine must be surgically removed which can further complicate nutritional problems because of short bowel syndrome.
Distal Intestinal Obstruction Syndrome (DIOS)
DIOS is a condition unique to people with Blockage of the intestine in children and adults also called meconium ileus equivalent because it is similar to MI. DIOS can result from mal-absorption.
DIOS may occur
- With changes in diet
- With dehydration or change in fluid intake
- With altered bowel habits
- With decreased physical activity
Symptoms of DIOS
- Abdominal pain
- Vomiting
- Mass of hard stool in the lower right abdomen
- Can result in intestinal rupture
- Lack of stool but not necessarily
- High risk of reoccurrence
Treatment of DIOS
- Early recognition of symptoms
- Aggressive use of enemas
- Surgery to remove blocked portion of intestine or damaged intestine
-
SBBO is a condition that occurs when there is an imbalance of good and bad bacteria (dysbiosis) in the intestine causing inflammation.
Symptoms include
- Watery diarrhea
- Gas, bloating
- Abdominal distention
- Excessive gas and discomfort
Causes include
- Use of antibiotics especially recurrent use
- Mal-absorption
- Gastrointestinal surgery and short bowel syndrome
Treatment
- Antibiotics that work on gut bacteria
- Probiotics
- Therapies to improve absorption
-
- CF Liver Disease occurs in about 10 percent of patients with CF
- Recurrent Pancreatitis occurs in a minority of pancreatic sufficient patients
Endocrine Issues
Cystic Fibrosis Related Diabetes (CFRD)
Cystic Fibrosis Related Diabetes is a unique form of diabetes that occurs frequently in people with CF. It shares features of both Type 1 diabetes and Type 2 diabetes but it is very different from these forms of diabetes in many ways
- Causes
- Prevalence
- Symptoms
- Screening and Diagnosis
- Treatment
Pubertal Delay
CF Bone Disease
- Osteopenia and Osteoporosis
Social and Psychological Issue
Feeding Problems in Young Children
Problematic feeding behaviors occur more often in children with CF and other chronic diseases. The use of problematic feeding behaviors is associated with lower nutrient intake and lower weight in children with CF. Children use ineffective feeding behaviors to seek caretaker attention no matter how negative the attention may seem. Caretakers give increased amounts of attention to the child in response to these behaviors and so they are repeated.
Prevention of Behavioral Feeding Problems
- Start purees at 4-6 months of age
- Transition to soft table food starting at 8-10 months
- Transition to cup by one year of age
Maintain a separation of responsibility when feeding your infant or child
- The caretaker should be responsible for when and what food and beverages are offered and for providing a non-pressured, enjoyable family meal environment. The caretaker should also be aware that appetite may decrease because of any of the gastrointestinal issues common to CF as well as during illness.
- The child should be responsible for how much is eaten, which foods are eaten, and even if he or she is going to eat at all.
- Support your child with alternative feeding methods. It is not uncommon for caretakers to engage in ineffective feeding behaviors that result in less food intake rather than more and can cause a large amount of family stress.
Treatment for behavioral feeding problems
Recognize common ineffective feeding behaviors of young children and commonly employed but ineffective behavioral responses caretakers engage in.
- Child: Chatting instead of engaging in eating
- Parent: Prompting child to eat, take one more bite, eat his veggies etc
- Child: Repeatedly leaving the table or disrupting the meal
- Parent: Talking to the child and insisting they stay at the table and have to eat eat, eat one more bite, eat their veggies etc.
- Child: Drinking instead of eating
- Child: Not taking bites
- Parent: Urging, bribing, negotiating with the child to eat, eat one more bite etc.
- Child: Not trying, refusing novel or “non-preferred food”
- Parent: Urging, bribing, negotiating with child or forcing the child to eat the food, short order cooking, or providing only preferred food.
In each scenario the caretaker is giving his or her attention for a negative behavior.
Behavioral strategies that include ignoring negative behaviors and giving attention for positive eating behaviors have proven effectiveness in improving food intake and weight status in children with CF.
Positive reinforcement of specific behaviors by giving your attention when your child is eating and ignoring when not is a powerful tool in helping your child eat normally. Let your child know specifically what he or she is being praised for.
- "Good job taking that bite"
- "Good job eating your veggies"
- "I like the way you finished your meat so quickly"
- "I think it's great the way you take your enzymes when I put it by your plate"
- "Wow, I am so proud of you for trying those carrots"
Using these reinforcers with other good eaters at the table while ignoring the child who is not eating, refusing to try, demonstrates to your child how to get your attention in a positive way and that negative ways are not effective in getting your attention.
Your child may “push back” during this change in your behavior with even more attention seeking behaviors including screaming or throwing food. Continue to ignore these behaviors, hang in there, be consistent and the child will figure it out.
Some may need assistance from a skilled mental health professional
Overview
Accordion Content
When planning your clinic visit, please think about vacation or special event planning. We really don't want CF to interrupt your life if it can be avoided. So, if you have a vacation or trip planned, plan to come to clinic at least two weeks before the vacation or right after.
WEARING MASKS! - It is important to follow CFF infection control guidelines when coming to the medical center. Please remember to wear a mask for your own protection while in the clinic or hospital.
-
The pediatric CF clinic is located on the second floor in the Children's Health Institute of New Jersey (CHINJ).
Overview of Pediatric CF Clinic Days
The physical address is:
Child Health Institute of New Jersey
89 French Street, Suite 2300
New Brunswick, NJ 08901 -
The adult CF Clinic is located on the 5th floor of the Clinical Academic Building (CAB).
Overview of Adult CF Clinic Days
The physical address is:
Clinical Academic Building (CAB)
125 Paterson Street, Suite 5200B
New Brunswick, NJ 08901
Schedule an Appointment
CF patients under 1 year of age are normally seen 1x per month until 12 months of age, then every two months. Children, adolescents and adults are seen every two to three months or more frequently depending on your health status.
The scheduling line is open Monday through Friday, 8:30 am to 4:30 pm.
*If you need to cancel an appointment, simply call the scheduling line to cancel and request a reschedule. If you have difficulty rescheduling, please contact our office directly.
- Pediatric Pulmonary Scheduling: 732-235-7899
- Adult Pulmonary Scheduling: 732-235-7839, prompt 1
Developing a Care Plan
Many patients find that keeping a record of all medications and treatments is helpful in managing their health and remembering all there is to do. This plan can also be a helpful tool in clinic when changes are made to your/your child's healthcare regimen. You can work with your care team to review it at each clinic visit and make necessary changes.
Hospital Guide
Accordion Content
Having CF is not easy, nor is being in the hospital. Being in the hospital can be very difficult on you and your family. There are many things you will learn along the way, this is just a quick guide to aid you in the process of being admitted to the hospital. For more detailed information please see the links at the bottom of this page for the adult and pediatric patient guides.
-
You can expect that you/your child will be hospitalized anywhere between 7 and 14 days depending on their symptoms. Please plan accordingly.
The Emergency Room
Sometimes, illness strikes quickly and you cannot wait for a clinic visit. Both the pediatric and adult programs have an on call services 24 hours per day, 7 days per week for anyone who cannot wait for normal business hours to speak to a physician. In some cases, the emergency room is necessary. When this happens, please make sure to call the pulmonary service ahead of time to let us know you are on your way. We can reach out to the emergency room clinicians and help prepare them for your arrival and what might be needed. Please be advised that if you are over 21, you may be sent to the adult ER even if you are still followed in the pediatric program. As long as we know you are coming, your primary pulmonlogist will make sure you are admitted under the correct services.
It is also important to inform the clinicians in the ER that you have CF and should be in contact isolation while in the ER. Wait times can be long even within the emergency room so contact isolation is important.
Admitting
If you are admitted during normal work hours (9am to 5pm) you will be admitted into the hospital through the clinic. Should you arrive at the hospital after normal hours, you will need to be admitted through the Emergency Room in the Main Hospital. One of the clinic staff will make the ER staff aware that you will be arriving. You will go through the ER process as if you are a “regular patient”. Meaning you will need to see a triage nurse to go through a brief medical history, you will be given a patient ID bracelet and you will be seen by the on-call ER doctor prior to being given a main room.
PICC Lines
Please be aware that a PICC line will need to be inserted into your [child’s] arm to administer some of the IV antibiotics. Not all blood draws can be done through the PICC line. If you will be receiving sedation for the picc line, you must be fasting for 8 hours before the procedure (no eating OR drinking - even water). Plan your eating schedule accordingly prior to arriving to the hospital. Please click here for more information on PICC lines.
Often, our patients will go home to complete your IV therapy. When this happens, we will work with the home care company to manage your medications and maintain your picc line. Weekly blood draws will also be done at home and sent to our office. Your nurse will work closely with you in these situations to help you manage your care at home.
Contact Isolation
You/your child will have a private room and will be on contact isolation which means once admitted into your main room all hospital staff (doctors, nurses and pulmonary staff) should wear blue gown & gloves prior to entering you/your child’s room. This also means that CF patients are not permitted in the play room or the teen room. Any time you/your child leaves the room, you must wash your hands and wear a mask. This is for the protection of other patients as well as your [child’s] protection.
Enzymes
Enzymes can be kept in your room for convenience as CF patients will need to eat three meals and three snacks every day.
-
Rounds
Inpatient rounds start at 6am (visits from the doctor or other medical professionals) by the attending, or for the adults the Fellow (a fellow is a DR studying to become an attending). Inpatient CFRD screenings will occur for all CF patients 10 or older. Depending on other issues you/your child may have, other doctors may visit throughout the day (i.e. Endocrinologist, hematologist).
Respiratory Treatments
Nebulizer treatments and chest PT will occur 4 times a day. One treatment may occur while you are sleeping (either early in the morning or in the evening). If sleeping you will be woken. You need to be an active participant in your therapy whether at home or in the hospital. Please remember, whether you are in the hospital or on home IVs, we always recommend treatment four times daily while on IVs for maximum benefit.
PFTs
PFTs may be done prior to antibiotics and then up to twice more before you leave. Spirometry will be done once a week. This should be done with your morning treatment and can be done in the lab or your room, whichever you prefer. Please remember transportation can take up to 1 hour.
Meals and Snacks
Your [child’s] snacks are ordered after meeting with the nutritionist. (If you do not see a nutritionist the first day, be sure to tell your nurse or physician). Snacks usually arrive around the same time every day. Meals are ordered through room service from 6:30AM-8PM Monday through Friday and 6:30AM-6:30PM on the weekends.
Activities and Exercise
The pediatric rooms are equipped with a TV, XBOX, and a DVD player. Child Life Specialists can visit the room to assist with exercise; they can also bring additional games or toys, however supplies are limited and are only available for one day at a time. (PLEASE NOTE: this option is not available in the adult hospital.) In the adult hospital you will be required to pay a daily rate for the phone and TV. Calls from the hospital phone can make and receive calls from within the hospital. (i.e. To room service without renting the phone. There is a computer in the solarium that you are welcome to use.)
Hear from families about their experiences and advice about hospitalization.
Hospital Tips from a Mom
“Some things I have learned from my experience as a mom in the hospital"
If you are being admitted through the ER, call the CF center and your doctor or the doctor on call will alert the ER you are coming and the tests that need to be done. Time in the ER can be lengthy so bring a book or a kindle! Also, when heading the hospital bring a change of clothing & toiletries for yourself & child. Any comfort items your child likes, blanket/dolls, etc., books & things they enjoy doing. Each time we have gone to the ER we have been admitted to the hospital. So depending on your distance from the hospital, I would plan for the most instead of the least.
You will answer the same questions many times with the ER staff, when admitted to the floor and then when the rounds are done the next morning and through your stay. The initial intake takes the longest and it helps if you have a notebook with certain symptoms, doctor visits or a list of medication with names, dosage amount & times. Depending on your insurance, you might want to bring your medication with you to the hospital.
Regarding meals - you are able to bring food from home & store it in the large refrigerator in the kitchen or the small fridge all rooms have (a microwave is also available). Utensils & napkins are available but no plates. Also, the nurses have a book at the desk with the take out menus from the area to look through and all deliver to the hospital.
XBox game systems are in the rooms and games can be borrowed on a daily basis from the child life room as well as videos & DVDs.
E-cards are awesome and so easy. The hospital has a link and they will print out the cards that people email. My husband and I put the link on our Facebook pages and our daughter received actual cards from our friends and family that the hospital prints out - very cool. She got so many! It really made her feel good.
-
- Clothing
- Toiletries
- Enzymes (this usually takes a day or so before it is ordered to suit you/your child‘s needs.)
- Electronics - Cell Phone, Laptop (wireless connection available), handheld video games, etc.
- Child’s favorite toys, blankets, stuffed animals, pillows, etc.
- Activities appropriate for your child – (i.e. books, DVD’s, puzzles, etc.)
-
Parking
Is available at the main hospital parking lot. Parking is free the day of admission and will cost $2 per day if validated for 1 family member by the receptionist at the information desk. Patients admitted for more than 14 days will get a pass for free parking. PLEASE NOTE: Parking tickets MUST be validated to get the reduced rate. Parking rules change, when in doubt, ask, someone might be feeling lenient.
Food
All of your child’s meals are provided by the hospital. Parents and visitors are able to request a meal pass from the nursing staff that provides an employee discount in the main dining hall of the hospital. There are also dining facilities in the hospital as well as many excellent restaurants around New Brunswick.
Sleeping Arrangements
In the pediatric hospital, parents are welcome to stay in the room with the patient. Usually the rooms have a couch and recliner chair. In the adult hospital, spouse or family member (only 1 per night) are allowed to spend the night. You must recliner. Hospital blankets and pillows will be provided, you may also bring your own from home.
Pets
Pets are allowed to visit you during regular visiting hours in the hospital. Pets may not go up to the patient‘s room. All pets must be up to date on all shots and vaccinations. Security MUST have the paperwork BEFORE the pet arrives at the hospital. DO NOT bring them together, it will not work out well for you. Notify the head nurse and s/he can get the process started for you. NOTE: this may differ in the children’s hospital.
Laundry
There is a laundry room available in the children’s hospital. Please bring appropriate detergents if you would like to use the facilities. NOTE: this is not available in the adult hospital
Siblings
Siblings are welcome to visit. However siblings under the age of 18 are not permitted to sleep in the room. This policy can change during FLU season. Please call ahead during flu season to check visitors policy for children. Please make appropriate child care arrangements. Please note that siblings are welcome to stay at the Ronald McDonald House (see info below).
School Work
Please let the CF center social worker know if your child needs anything for school, letters, tutoring services, etc. We work with a foundation that can help to provide tutoring services during your stay and we regularly communicate with your school (Even if you are in college or graduate school). Arrangements can be made to have your child’s work sent to the hospital.
-
- Robert Wood Johnson Patient Guide for the adult hospital
- Bristol Myers Squibb Children's Hospital
Ronald McDonald House
There is a Ronald McDonald House in New Brunswick, across the street from the main hospital. The house is able to assist family with many amenities including additional sleeping and eating arrangements, however space is limited to six rooms. Families must outside a 10 mile radius from the New Brunswick house to be eligible to stay. Please call (732)249-1222 upon knowing of your need for admittance. IF a room is available, the staff at Ronald McDonald house will need a referral to be completed by current CF social worker.
Embrace Kids Foundation
Our CF Center has developed a partnership with a wonderful organization that has been working with patients and families at RWJUH for several years. Embrace Kids Foundation is a non-profit organization originally established to help children living with Cancer and blood disorders. However, they have broadened their scope and have offered a great deal of support to our pediatric patients and families. They can help with tutoring, visiting during your stay, setting up a buddy group for your child, and much more. Click on the above link for more information and talk to the social worker if you would like to get involved with this group.
Overview
Living with a chronic disease brings many challenges throughout the lifespan for the whole family. Your CF team is here to help with those challenges, whether they are medical, emotional, educational, financial or employment related. Our licensed clinical social worker is available at any time to talk with you, either in clinic or by phone or appointment. If we don't have the resources you need here, we can help connect you. Below is a list of most commonly used resources but this is not intended to be an exhaustive list. Please contact your CF social worker for more information.
Resources
Accordion Content
-
- www.cff.org - General Information, Advocacy, Patient Assistance, research and center specific information
- CFF - Compass - Case management, advocacy and resources for patients and families through the CF Foundation
- The Healthwell Foundation is a non profit organization which can provide funding for certain CF treatments, equipement and nutritional supplements for CF patients who qualify financially. Please ask the social worker in our center for more information or go to their website to apply directly.
- www.cysticfibrosis.com – recipes, section for kids, parenting survey, Know CF
- www.thelittleacorn.com – offers journals for tracking care, visits, hospitalizations, etc. for patients with specific health conditions. Journals are sold, they are not free.
- www.parentingchildrenwithhealthissues.com – Website with informational articles on parenting issues for families with children with health care issues. Also offers a book called, “Love and Logic” by Dr. Foster Kline.
- Blooming Rose Foundation – Provides social services, positive contacts and hope to families immediately after diagnosis.
- FACEBOOK – CF Foundation has its own site on Facebook and many patients connect with other CF patients and families through Facebook. Please remember that facebook is not a supervised website so younger people should be monitored.
-
- www.njsocf.org – NJ State Organization for Cystic Fibrosis. Non-profit, state and privately funded group established to assist patients 18+ with CF with medications, co-pays, equipment, nutritional supplements, groceries, etc. Applications available online. Assistance to families with children under 18 is available up to $2000 per year. Please ask Erin for more details.
- www.cfpaf.org – Cystic Fibrosis Patient Assistance Foundation, sponsored by the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation. Offers financial assistance for specific medications and links to assistance for other meds and equipment, as well as advocacy and case management.
- www.panfoundation.org – Patient Access Network, set up to assist with co-pays for specific medications. Please ask Erin for more details.
- www.genentechaccesssolutions.com – Program set up by Genentech to provide assistance to patients in paying for Pulmozyme.
- Podcare Plus – Ask Erin for more information or call 1-877-999-8624 to register. All patients who have cultured Pseudomonas and are taking Tobi are eligible for this program.
- www.cayston.com/cayston-access-program.html Cayston Access Program – Brings co-pays down to $25 for most CF patients. Prescription must go through Cayston Access Program. Also has foundation that will pay for drug for uninsured patients.
- www.creon.com/CFPatients/EnrollInCFCareForward - CF Care forward program enrollment page. Copay assistance for insured patients, foundation assistance for uninsured and free supplements and vitamins monthly for those using Creon
- www.live2thrive.org – Zenpep patient support program. Copay assistance for insured patients, foundation assistance for uninsured, and free vitamins and supplements monthly for those using Zenpep.
- www.needymeds.org – Non-profit that offers information on free and low cost drugs. This is usually a link to a foundation or manufacturer. They also offer the free needy meds drug discount card, which provides up to 75% discount on prescription medications for those who do not have insurance.
- www.thelivingbreathfoundation.com – This foundation supports research, medical assistance, scholarships and financial aid.
- www.changealife.org – Change of Life Foundation – Mission of founder is to inspire and challenge grant recipients to follow his charitable example and one day repay the favor by helping others in need.
- www.cflf.org – Foundation that provides financial assistance to individuals and possibly a “support person” for gym membership of some athletic activity. Grants are usually up to $500 per year and you can reapply yearly.
-
- https://www.hhs.gov/regulations/index.html: A Guide through the new healthcare legislation. Very useful for all regardless of the type of insurance you currently have.
- CF Legal Hotline – (800-622-0385). This is a great source, headed by Beth Sufian, CF patient and advocacy lawyer. Hotline is expert in advising around insurance issues, disability, medicare/medicaid, school laws, employment issues, COBRA insurance, HIPAA, FMLA and the new healthcare legislation. Email address is cflegal@cff.org
-
-
www.AbbVieCFScholarship.com/apply - Applicants include U.S. citizens with CF who are enrolled or awaiting acceptance from an accredited institution in the fall. Awards are based on applicants’ creativity, academic excellence, community involvement and ability to serve as a positive role model for the CF community.
- www.elizabethnashfoundation.org - awards scholarships to assist persons with CF to pursue undergraduate and graduate degrees. Scholarships are awarded on the basis of demonstrated need and accomplishment, both academic and other. Grants are made each year to people with CF who exhibit clear academic goals and a commitment to participate in activities outside the classroom. Grants are made directly to the academic institution to assist in covering the cost of tuition and fees
- Boomer Esiason Scholarship programs The Boomer Esiason Foundation has multiple scholarship opportunities for people with various talents and needs.
- Scholarship Fund | New Jersey State Organization of Cystic Fibrosis - The NJ State Organization for Cystic Fibrosis has started a scholarship fund for NJ residents.
-
Research
The Cystic Fibrosis Center at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School is a designated center for the TDN (Therapeutics Development Network).
The Cystic Fibrosis Therapeutics Development Network (TDN) is the largest cystic fibrosis clinical trials network in the world.
The TDN brings together experts from across the United States to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of new CF therapies through clinical studies. We work continually to improve research methods and pursue new areas of scientific inquiry.
Through efficient study design, optimized clinical trial execution and high-quality data, the TDN helps speed the delivery of new and better therapies to people with CF.
This center, along with many CF centers around the country, is involved in multiple clinical trials to develop new drugs to treat this disease. For more information on CF related research, please go to: Therapeutics Development Network (TDN) | Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Therapeutics.
If you have questions about your eligibility to participate in a research study, please talk to your CF team.
To search clinical trials, you can also go to Clinical Trial Finder.
Fundraising

Looking for a great way to get your family more involved with the local community? Searching for a serious challenge that will push you mentally and physically? Or just want to contribute to a worthy cause?
You’ve come to the right place. Each year, thousands of volunteers, families, coworkers and friends come together at exciting fundraising events to help add tomorrows to people living with cystic fibrosis — and you can, too.
The Cystic Fibrosis Foundation offers a number of unique opportunities that fit a range of interests, budgets and lifestyles. Find the event that’s right for you and get involved today!
For information on the various fundraising campaigns that the CF Foundation is involved in, go to: Foundation Events | CF Foundation.
Our center participated in the Great Strides Walk every year to support the NJ Chapter of the CF Foundation. We encourage all of our families to join us at this great event. Your center coordinator can give you more details about walk locations and dates in New Jersey.
Emotional Health

CF is a Multi-system disease that affects every area of your body and your life. Despite new drugs to “modify” the effects of this disease, management of CF is complex and time consuming (averaging 2-4 hours per day). As a result, CF continues to be one of the most difficult chronic conditions to manage. Studies measuring psychological distress in individuals with CF , and their parent caregivers, have found high rates of both depression and anxiety. Psychological symptoms in both individuals with CF and caregivers have been associated with decreased lung function, lower BMI, worse adherence, worse quality of life and more frequent hospitalizations. (Quittner AL, et al., 2015)
The TIDES study was an international study, sponsored by the CF Foundation and the European CF Society, which looked at the prevalence of anxiety and depression in CF.
- Screened over 6000 patients ages 12 and older and 4000 parents.
- Indicated higher rates for both depression and anxiety
- Higher rates of anxiety
Important Finding: When parents report elevated depressive or anxiety symptoms, their adolescent with CF is more than twice as likely to experience depression and anxiety (Quittner AL, et al., 2015).
A panel of experts worked together over 18 months to:
- Review the research
- Develop recommendations for clinical care
The Panel developed 15 recommendation statements for screening and treatment of depression and anxiety in individuals with CF and parent caregivers (Quittner AL, et al., 2015).
Consensus Statement
Periodic screening of depression and anxiety symptoms and appropriate interventions can significantly improve quality of life and health of individuals with CF and their parent caregivers
- All CF Centers have been asked to provide ongoing support and education to all patients and families to promote stress management, health coping skills, etc.
- The Cystic Fibrosis International Guidelines Committee recommends the following for screening and treating depression and anxiety as part of comprehensive CF care:
- Learning new coping skills
- Getting screened
- Getting help
- All CF centers will initiate a screening program for anxiety and depression to include annual screenings during clinic visits conducted by the clinical social worker to all patients 12 years and offered to parent caregivers of patients 0-17 years old. (Parent/family screening is optional)
- PHQ-9 to screen for depression
- GAD-7 to screen for anxiety (Quittner AL, et al., 2015).
- Results will be reviewed with you in clinic and will fall into one of three categories:
- Normal Screening- proceed to get annual screening
- Mild Range- receive supportive intervention and will be rescreened at next visit
- Elevated range- receive clinical assessment and psychological and/or psycho-pharmacological interventions
- Recommendations include a stepped care model for anyone who is experiencing higher than average levels of depression or anxiety
- Recommendations also include detail on the types of therapeutic interventions that have been found to be the most effective
- Our center received a grant for three years to help fund a screening and follow up program. This gives us the ability to:
- Hire our social worker to work full time
- Hire a psychologist to help with counseling needs
- Screenings will be kept confidential and will be repeated annually when “normal” or more frequently if elevated
- We will work closely with you to get additional support
Guides to Help You
Staying Healthy
Promote Emotional Wellbeing
- Foster resilience: through purpose, setting expectations, letting go and savoring the good
- Self compassion: studies show that people who have compassion for themselves are happier, more optimistic and more grateful vs. self criticism: leads to higher rates of depression and stress, with less effective coping
- Self acceptance: reduces your battle with yourself, frees you to be more peaceful and happy
- Learn mindfulness: or relaxation practices that soothe and center you
- Healthy lifestyle: Exercise, Sleep, and Eat!
- "Neurons that fire together, wire together" : Change your thoughts and you will change how you feel
- Be flexible: expect the unexpected, redefine "success" to find your happiest life
- Acknowledge fear: and develop inner strength
Locations
Cystic Fibrosis Center
Medical Center Director - Thomas Scanlin, MD
Child Health Institute of New Jersey
89 French Street
New Brunswick, NJ 08901
Appointments: 732-235-7899
Adult CF Center
125 Paterson Street. 5th Floor
New Brunswick, NJ 08901
Appointments: 732-235-7840
Pediatric/Adolescent Program Staff
| Title | Name | Phone | |
| Director | Thomas Scanlin, MD | 732-235-7899 | |
| Associate Director | Maya Ramagopal, MD | 732-235-7899 | |
| Assistant Professor | Lakshmi Uppaluri, MD | 732-235-7899 | |
| Center Coordinator/ Social Worker |
Erin McElroy Barker, LCSW | 732-235-6409 | mcelroer@rutgers.edu |
| Nurse Practitioners | Chinwe Izegbu, APN, FNP Dawn Tortajada, APN, CPNP | 732-235-5041 732-235-7899 | cmi35@rwjms.rutgers.edu dawn.tortajada@rutgers.edu |
| Registered Dietician | Registered Dietician | 732-235-6241 | mintzda@rwjms.rutgers.edu |
| Respiratory Therapist | Eddy Paredes, RRT | 732-235-5235 | ekp33@rwjms.rutgers.edu |
Adult Program Staff
| Title | Name | Phone | |
| Program Director | Sabiha Hussain, MD | 732-235-7840 | |
|
Assistant Director |
Sugeet Jagpal, MD | 732-235-7840 | |
| Nurse Practitioner | Chinwe Izegbu, APN, FNP | 732-235-5041 | cmi36@rwjms.rutgers.edu |
| Pulmonary Nurse | Cathy Trillo, RN | 732-235-7840 | |
| Center Coordinator/ Social Worker |
Erin McElroy Barker, LCSW | 732-235-6409 | mcelroer@rutgers.edu |
| Registered Dietician | Rachna Singh, RD, CDE | 732-235-5539 | singhra@rwjms.rutgers.edu |
| Respiratory Therapist | Paula Marulanda, RRT | 732-235-7970 732-235-6377 | marulapa@rwjms.rutgers.edu |
Additional Professional Staff
The following team members cover both pediatric and adult programs but are here on a limited basis. Please feel free to reach out to them directly or request to see them during your next clinic visit.
| Psychologist | Amanda Morales-Clark, PsyD | amandmor@rwjms.rutgers.edu |
| Physical Therapist | MaryJane Myslinski, PT, EdD | myslinsk@shp.rutgers.edu |
| Pharmacist | Eileen Harrington, | eh444@rwjms.rutgers.edu |
Additional Contact Info
Weekdays 8:30 AM to 4:00 PM:
- To Reach the Adult Program - Dial 732-235-7840
- To Reach the Pediatric Program - Dial 732-235-7899
Sick Calls
For Sick Calls, please use the MAIN NUMBER and follow prompts for the nurses line during office hours, and the service during off hours. Leaving messages on a staff members personal line WILL NOT guarantee a call back. If a nurse is unable to answer the line at that moment, please leave your name, phone number, the patient's name, date of birth and what the problem is. A nurse will call you back as promptly as possible. If you do not receive a call back in a timely fashion, please do not hesitate to call back and try to speak to somebody. If you need to reach a physician after hours, please follow the prompts to call the answering service.
For Prescription Renewals
Please call the above number and follow the prompts for prescription renewals. Call our staff at least 1 business day before your prescription is about to run out (longer for mail orders). We will need to know the pharmacy telephone number, the names of the medications needed and your/your child's date of birth. Please specify whether the prescription is for 30 or 90 days.
For Scheduling Appointments
Please call the designated program and make an appointment with the pulmonary scheduler. Inform the scheduler that your child has CF so that you/your child gets an appropriate appointment time and day. If you need an appointment urgently or cannot get an appointment through the appointment line, please call our office and we will assist you.
Weekdays 4:30 PM to 8:30 AM and Weekends and Holidays
Please call the above numbers and the answering service will page the physician on call. Please call only with an emergency or illness. Non-urgent messages will be answered the next day and Prescriptions will not be REFILLED during non-business hours.
* If you have trouble getting through the phone system, please let us know so that we can rectify the problem.
* We will make every effort to call you back/ call in your prescriptions as soon as possible. We get many calls each day and need to return the most urgent calls first. Depending on the activities of the Center on any day, non-urgent calls may need to be returned later in the day
